Fluorescein Angiography
What is Fluorescein angiography?
Fluorescein angiography is a type of photography used to analyze retinal blood vessels. The test uses an orange dye called fluorescein. The dye is injected into the body and travels through all of the blood vessels in the body including the ones in the retina. Pictures of the dye traveling though the eye is obtained using a special camera and filters. The pictures are taken as a rapid series of timed images to allow a complete assessment of the health of the retinal vascular system.
How is Fluorescein angiography performed?
First the pupils of your eyes are dilated with eye drops to allow for the best pictures possible. Then you are seated in front of the camera and the fluorescein dye is injected into a vein in the arm. Pictures are taken as the dye flows through the blood vessels in your eye. The entire test takes approximately 15 minutes.
When is Fluorescein angiography used?
Many retinal diseases involve abnormalities to blood vessels overlying, inside or underneath the retina. Fluorescein angiogram is one of our most important tests that we have to help analyze any abnormalities in the retinal blood vessels. The results are used to diagnose disease and also to help plan for treatment. Of primary importance is the identification of dye leakage from previously normal blood vessels, which are now diseased (such as in diabetic retinopathy) or from new abnormal blood vessels (such as in macular degeneration) (figure 2).
What are the side-effects of Fluorescein angiography?
The fluorescein dye is removed from the body by the kidneys, so urine is commonly yellow or orange for 1-2 days. The skin and whites of the eyes may also appear slightly yellow for a few hours.
What are the risks of Fluorescein angiography?
About 1% of people can have a mild allergic reaction to the fluorescein dye. Typically there is some itching or a few hives. Benadryl will usually control these symptoms.
Figure 1. Obtaining a Fluorescein angiogram.
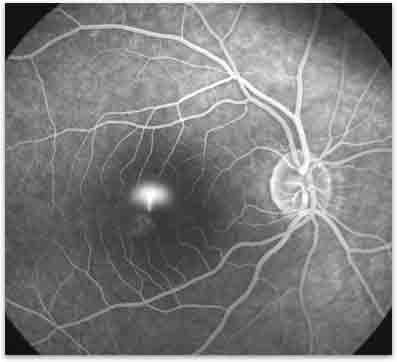
Figure 2. Fluorescein angiogram of Central Serous Chorioretinoapthy.

